Market research survey data can be broken down into two categories: qualitative and quantitative.
Qualitative Research data is usually gathered from open-ended questions in the form of opinions and descriptions, written in the participants’ own words. While this provides wider context and new ideas, qualitative data cannot be statistically analysed as it doesn’t a structured format for answers. For example: “Do you have any suggestions for how we can improve?”
Quantitative Research data focuses on numbers and statistics, which is easier to analyse with a survey platform because it relies on questions with specific answer options that can be quantified later. For example: 75% of participants “agree” or “strongly agree” that your product selection meets their needs.
Quantitative Research and Qualitative Research go hand in hand because they gather information in different ways, giving you a clear understanding of participant perception with scope for expansion and context in their own words.
With this distinction in mind, let’s explore further.
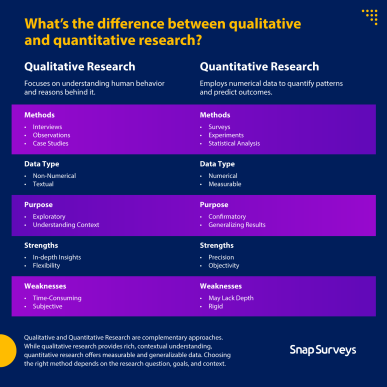
Qualitative Research
Qualitative Research is primarily exploratory research. It is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations.
It provides insights into the problem or helps to develop ideas or hypotheses for potential quantitative research.
Qualitative Research is also used to uncover trends in thought and opinions, and dive deeper into the problem.
Some common methods of qualitative research includes focus groups (group discussions), individual interviews, and participation/observations.
The sample size is typically small, and respondents are selected to fulfil a given quota.
Qualitative Research key points
Objective/Purpose
- To gain an understanding of underlying reasons and motivations.
- To provide insights into the setting of a problem, generating ideas and/or hypotheses for later quantitative research.
- To uncover prevalent trends in thought and opinion.
Sample
Usually a small number of non-representative cases. Respondents selected to fulfil a given quota.
Data Collection / Analysis
Unstructured or semi-structured techniques e.g. individual depth interviews or group discussions.
Non-statistical.
Outcome of Qualitative Research
Exploratory and/or investigative. Findings are not conclusive and cannot be used to make generalizations about the population of interest. Develop an initial understanding and sound base for further decision making.
Quantitative Research
A problem is aimed to be quantified by Quantitative Research through the generation of numerical data or information that can be converted into usable statistics. Within the research, facts are established and patterns are uncovered through the utilization of measurable data.
The data collection methods for Quantitative Research are more structured than those for Qualitative Research, encompassing various forms of surveys such as online, paper, mobile, and kiosk surveys. Other methods include face-to-face and telephone interviews, longitudinal studies, website interceptors, online polls, and systematic observations.
Quantitative Research key points
Objective/Purpose
- To quantify data and generalize results from a sample to the population of interest.
- To measure the incidence of various views and opinions in a chosen sample.
- Sometimes succeeded by qualitative research, further exploration of some findings is facilitated.
Sample
Usually a large number of cases representing the population of interest. Randomly selected respondents.
Data Collection & Analysis
Structured techniques such as online questionnaires, on-street or telephone interviews.
Statistical data is usually in the form of tabulations (tabs). Findings are conclusive and usually descriptive in nature.
Outcome of Quantitative Research
Used to recommend a final course of action.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research infographic
Download and share this handy infographic as a quick guide. To do this, click the image, then click the share icon in the view screen to share or download.